Migrating Bitbucket to Kubernetes
This document explains the process of migrating an existing Bitbucket installation to Kubernetes.
💡
Bitbucket 8.9.26 → 9.4.7
Pre-configured resources
- Rook ceph(Block, Filesystem)
- cert-manager
- Nginx ingress controller
- DB(PostgreSQL)
Helm Chart
Version: v3.17.3(GoVersion: go1.23.7)
Add the Helm chart repository
helm repo add atlassian-data-center \
https://atlassian.github.io/data-center-helm-chartsCheck Atlassian product version with chart version
helm search repo atlassian-data-center/bitbucketGet values.yaml command
helm show values altassian-data-center/bitbucket --version 1.22.0 > values.yamlEditing values.yaml
Modify according to your configuration.
Create namespace
kubectl create ns atlassianDeploy helm chart
Bitbucket version: 8.9.26
helm install bitbucket \
atlassian-data-center/bitbucket \
-f values.yaml \
-n atlassian \
--version 1.22.0Edit Bitbucket statefulset scale
kubectl scale statefulset --replicas 0 -n atlassian bitbucket💡
"Why is the StatefulSet's replicas set to
To prepare for migration by creating an empty Persistent Volume (PV), similar to the guides for Jira, Confluence, and Crowd.
The initial setup screen does not appear, so the replicas are immediately set to
0 immediately after deploying the Bitbucket Helm chart?"To prepare for migration by creating an empty Persistent Volume (PV), similar to the guides for Jira, Confluence, and Crowd.
The initial setup screen does not appear, so the replicas are immediately set to
0.Data Migration
Process for importing existing application data and using it in the existing environment
Migration strategy
- Bitbucket deploy(replicas=1 → replicas=0) with empty data(application-data, shared-home)
- Deploying a BusyBox pod with Bitbucket's local-home and shared-home mounted (I used a Debian image instead of BusyBox, as I’m more familiar with it)
- Get the application-data directory from the as-is Bitbucket instance and rsync it into the Bitbucket volume using a BusyBox pod
- Get the shared-home directory from the as-is Bitbucket instance and rsync it into the Bitbucket volume using a BusyBox pod
- Rescale Bitbucket statefulset(
replicas=0→replicas=1) - Check Bitbucket data
- Rescale Bitbucket statefulset(final replicasCount)
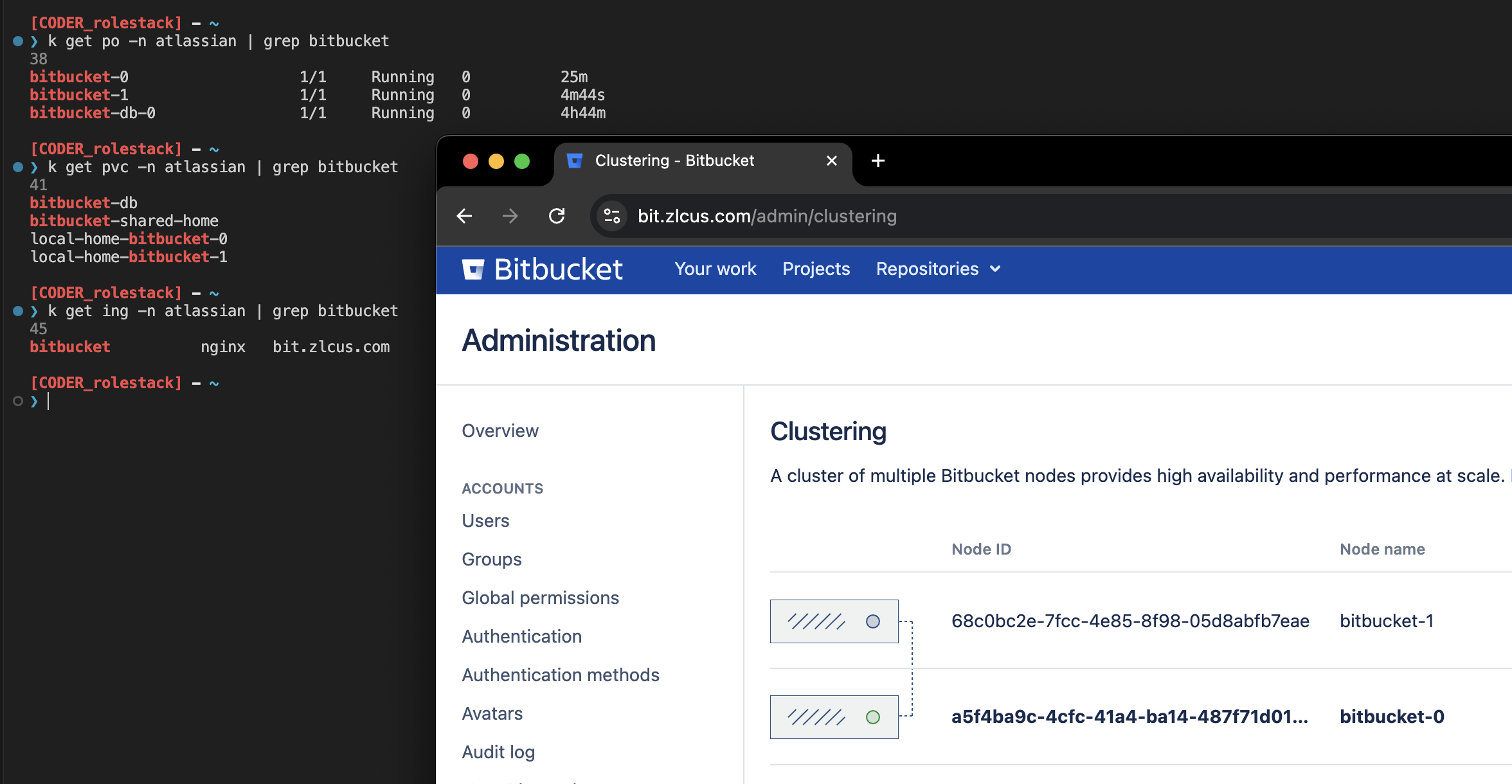
Upgrade
Upgrade strategy
- replicas 0(shutdown all Bitbucket pod)
- Set
image.tag - Helm chart upgrade
- Bitbucket statefulset scaling
Shutdown all Bitbucket pod
kubectl scale statefulset --replicas 0 -n atlassian bitbucketFor a Rolling upgrade, adjusting the replicas is not necessary.
Set image.tag
If you previously set image.tag but the APP VERSION matches the version you want to upgrade to, proceed with this step.
image:
# -- The Docker Crowd Docker image to use
# https://hub.docker.com/r/atlassian/crowd
#
repository: atlassian/crowd
# -- Image pull policy
#
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# -- The docker image tag to be used. Defaults to appVersion in Chart.yaml
#
tag: ""values.yaml
Helm chart
Bitbucket version: 8.9.26 → 9.4.7
helm upgrade bitbucket \
atlassian-data-center/bitbucket \
--version 2.0.2 \
-f values.yaml \
-n atlassian🗒️
During
The previous
helm upgrade, pods are created based on the replicaCount in values.yaml, and the first pod performs the upgrade task.The previous
--replicas 0 setting is ignored.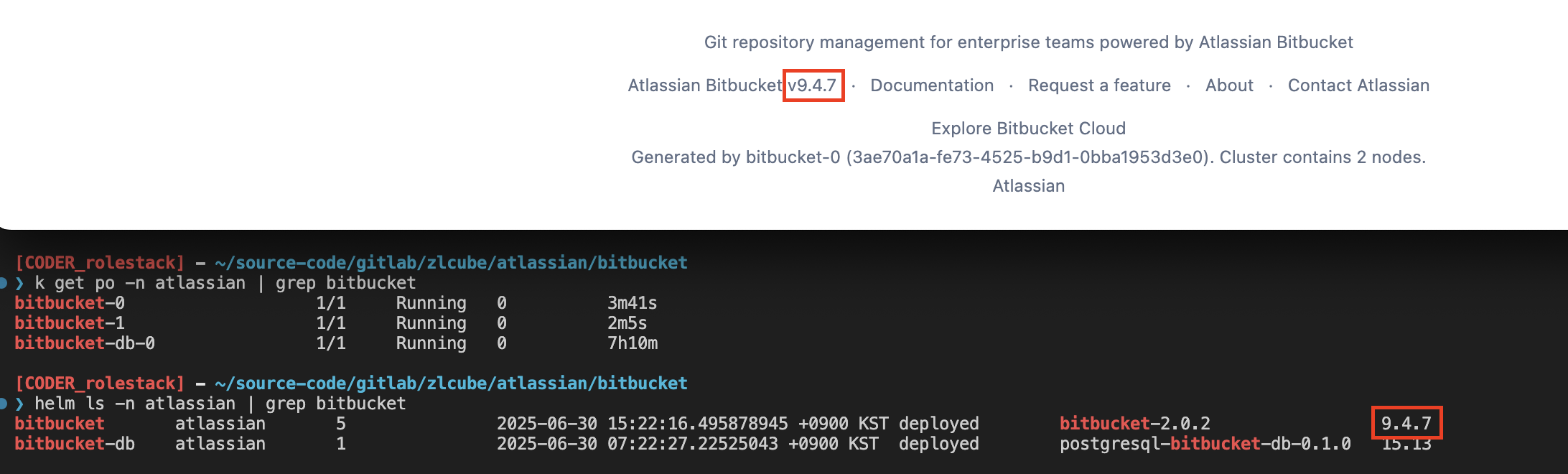
Using Bitbucket SSH with Kubernetes
In my case, I configured Bitbucket SSH access using OPNSense port forwarding combined with MetalLB.
The values.yaml file provides options to enable SSH access to Bitbucket.
sshService:
# -- Set to 'true' if an additional SSH Service should be created
#
enabled: true
# -- Port to expose the SSH service on.
#
port: 22
# -- The hostname of the SSH service. If set, it'll be used to configure the SSH base URL for the application.
#
host:
# -- SSH Service type
#
type: LoadBalancer
# -- Use specific loadBalancerIP. Only applies to service type LoadBalancer.
#
loadBalancerIP: <The LoadBalancer IP you will assign>
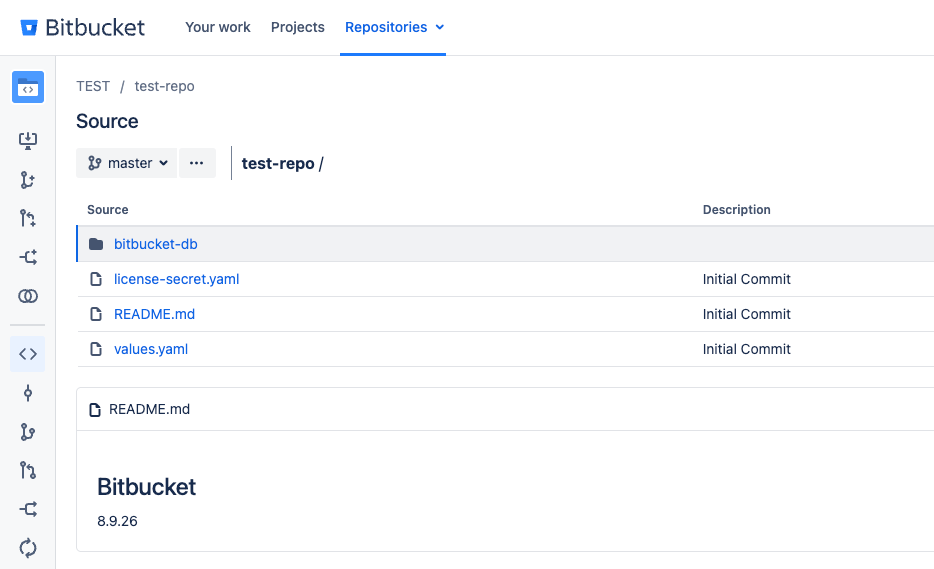
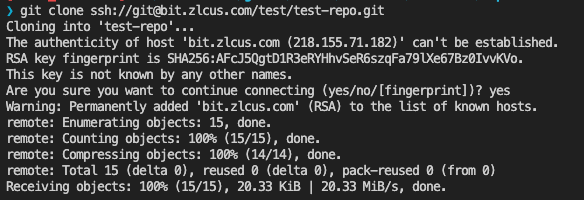
git clone over SSH.Reference
Products upgrade - Atlassian DC Helm Charts